
Taiyo Kogyo Column
How farmers can improve their earnings by utilizing the MAFF’s “Production Area Production Base Power Up Project”.
2020.11.17

Table of Contents
If we could install more expensive machines and facilities, we could generate more revenue…”
We want to rehabilitate our agricultural greenhouses and pass them on to the next generation!”
There is a system that we would like such farmers to know about. Have you ever heard of a subsidy program called the “Power Up Production Base Project for Production Areas”?
Please read through this article and don’t be put off by the mere mention of the word “grant. We will provide detailed and concise tips on how to improve profitability.



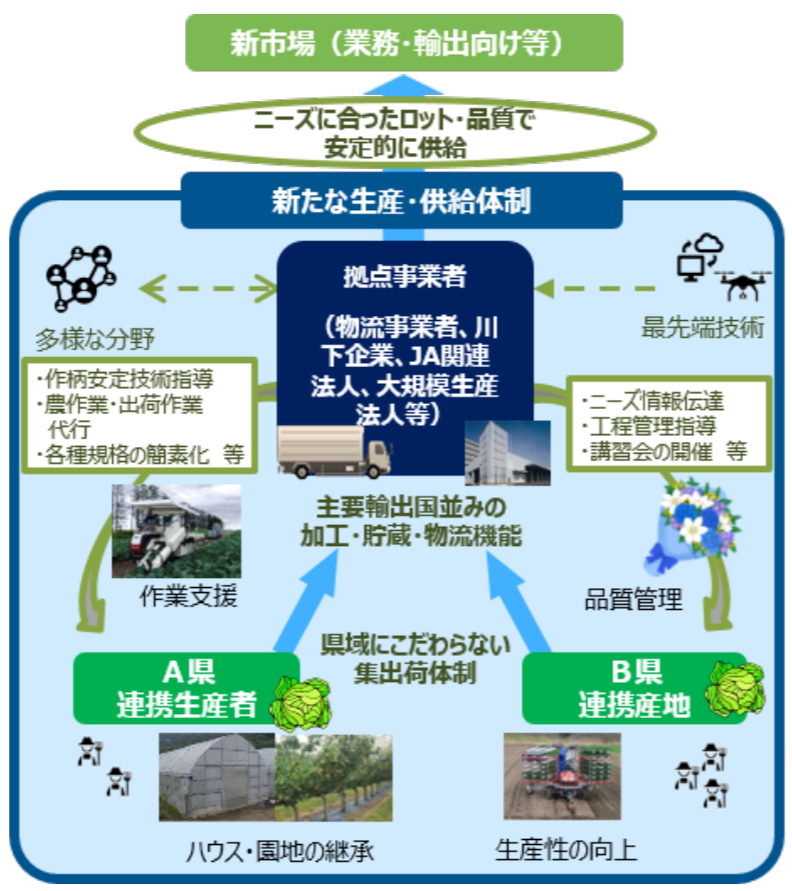
(Source: Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries website)
Outline of Collaborative Project Plan
The collaborative project plan will be developed in the following steps.
(i) Forming a group of farmers, etc. that has the following three functions and cooperates with the base business operators who provide production support, etc.
- Production stabilization and efficiency functions
- Supply adjustment function
- Function to meet the needs of actual customers
(2) Prepare a plan within three years that sets goals that meet the following two criteria.
- Increase the ratio of shipments to exports to total shipments by an average of at least 1 percentage point per year
- Increase the ratio of shipments for processing and commercial use to total shipments by an average of at least 3 percentage points per year, and begin export initiatives by the target year
(iii) Approval of the Director-General of the Production Bureau, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries
Supported by
- Base operators positioned in the above collaborative project plan
- Its collaborators (farmers, private businesses, etc.)
Subsidy Rate and Maximum

As the name suggests, “Measures to Improve Profitability” subsidizes the cost of installing necessary agricultural machinery and improving collection and shipping facilities for farmers who make plans to strengthen their profitability and work toward achieving this goal.
For example, they will financially subsidize a certain percentage of the following activities
- Development of key facilities in the production area, such as agro-processing and processing facilities and low-cost weatherproof greenhouses
- Lease introduction and acquisition of agricultural machinery
- Introduction of production materials
The support will be provided on the two main conditions that the “Outcome Goals” meet the criteria described below, and that the “Area Requirements” and other conditions are met.
Supported by
Farmers participating in the “Production Area Power Up Plan (Profitability Improvement Type)” prepared by the Regional Agricultural Revitalization Councils, etc., and farmers’ organizations such as the following are eligible.
- agricultural cooperative
- agricultural cooperative
- qualified agricultural land ownership corporation
- Other organizations organized by farmers
Individual management entities are also eligible to participate.
outcome objective
The entire production area must set goals that fall into one of the following seven categories and develop and implement a plan to achieve them. It is important to note that this is not the goal of the farmer or agricultural organization installing the machinery or equipment, but the goal of the entire production area.
- Reduction of at least 10% of production costs or collection, shipping, and processing costs
- Increase of 10% or more of sales or income
- An increase of at least 10% of the percentage of contract cultivation and at least 50% of the percentage of contract cultivation
- 100% conversion rate from products and varieties expected to decrease in demand to products and varieties expected to increase in demand
- If there is an export track record, an increase of 10% or more in the volume or value of shipments destined for export
- If there are no new export initiatives or no export results in the most recent year, at least 5% of total shipments or at least 10 tons per year of shipments for export.
- At least 10% increase in labor productivity
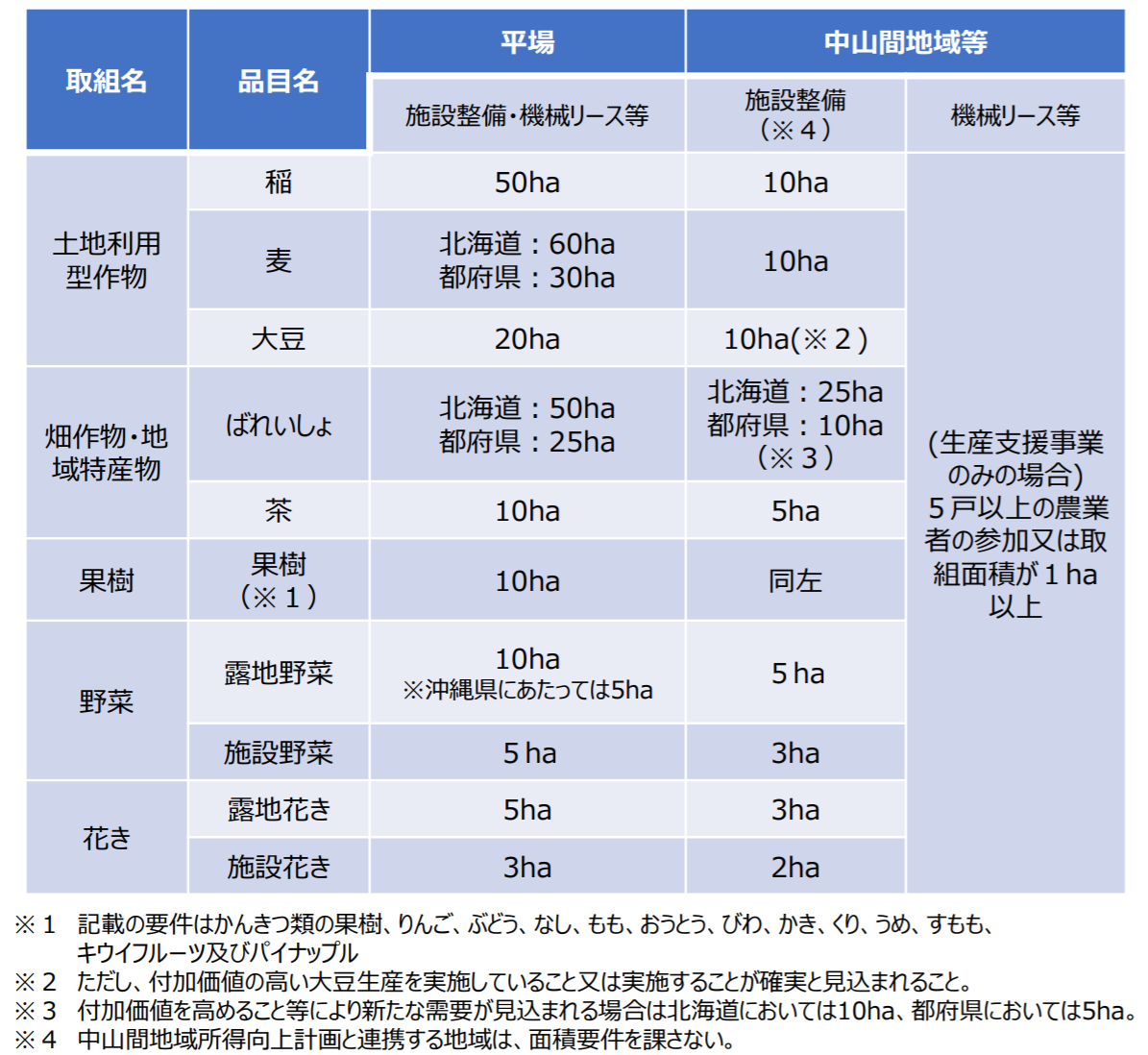
Area requirements are set individually for each commodity, with further exceptional measures to relax the requirements under certain conditions. For example, if the project is implemented in a mountainous area, the area requirement is relaxed as shown in the table below.
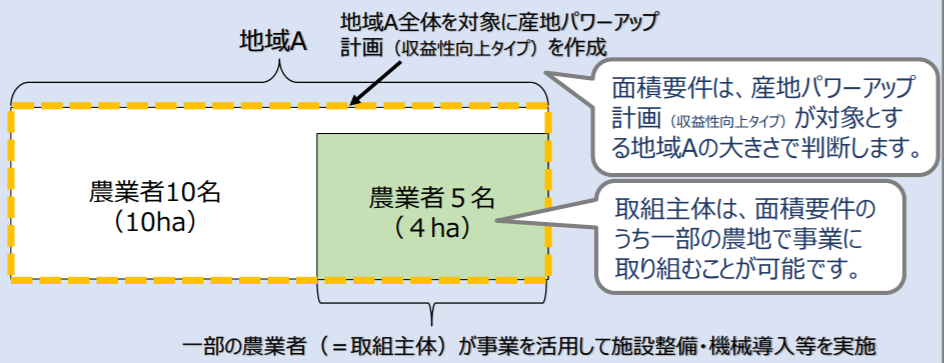

Initiatives eligible for support
The two main types of projects are defined as “maintenance projects” and “fund projects (production support projects and effectiveness promotion projects)”.
Maintenance projects
- Development of drying and preparation facilities
- Development of grain drying, preparation and storage facilities
- Development of collection, shipping and storage facilities
- Development of agricultural product processing facilities
- Development of facilities for advanced production technology (low-cost weatherproof greenhouses, etc.), etc.
Fund projects (production support projects and effectiveness promotion projects)
- Leasing and acquiring high-performance agricultural machinery to reduce costs
- Introduction of production materials required for high value-added production, such as rain shelter greenhouses
- Replanting of competitive varieties of fruit trees with the same varieties, etc.

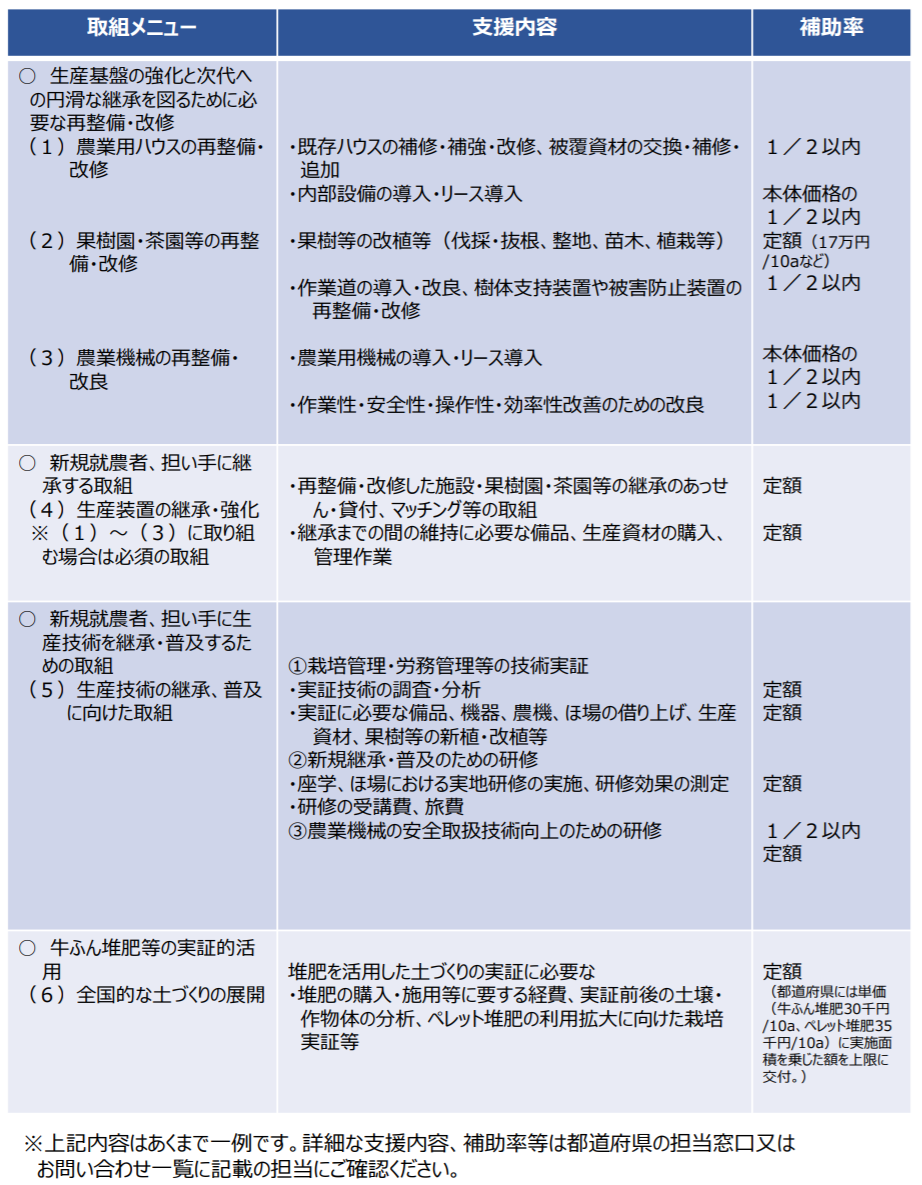

Farmers participating in the “Production Area Power Up Plan (Production Base Strengthening Type)” prepared by the Regional Agricultural Revitalization Councils, etc., and the following farmers’ organizations are eligible.
- agricultural cooperative
- agricultural cooperative
- qualified agricultural land ownership corporation
- Other organizations organized by farmers
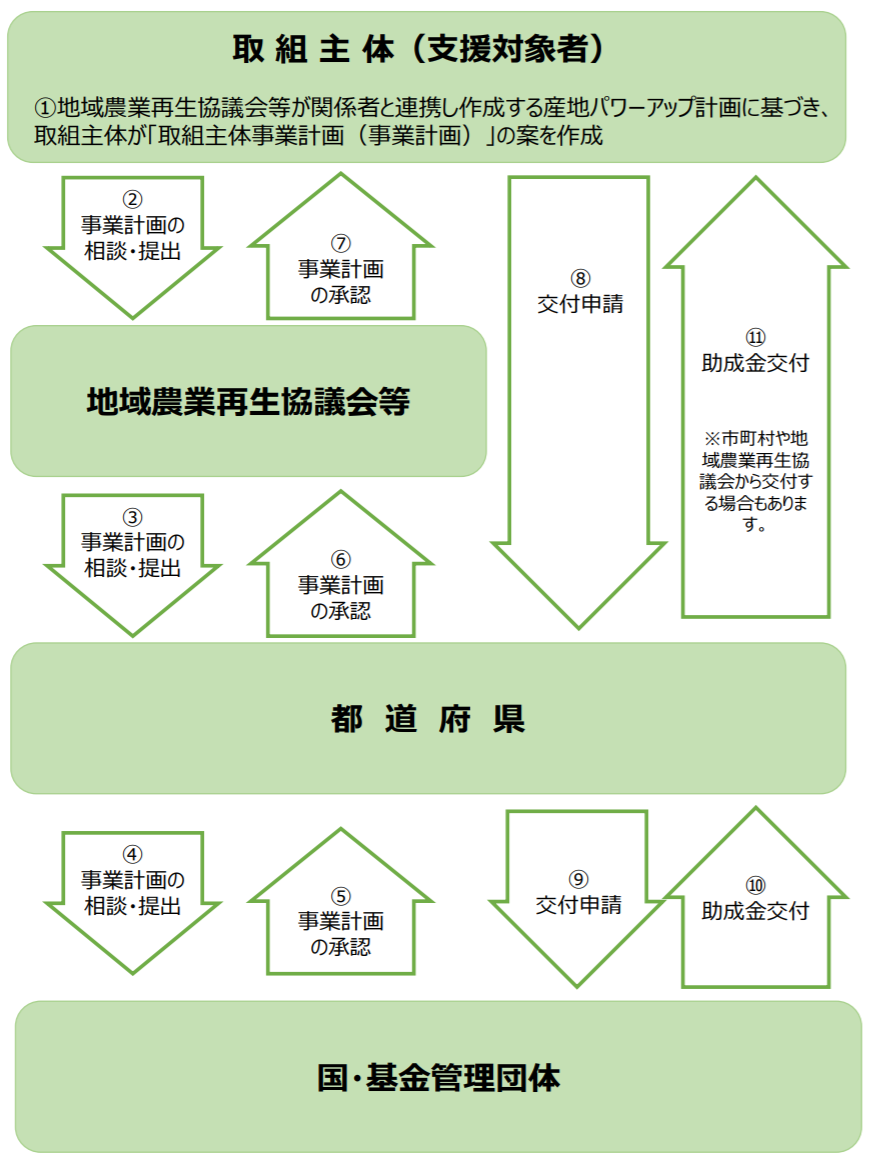

Regardless of which policy is used, the following procedures are to be followed when applying for the “Production Area Production Base Power Up Project”. Although it may seem complicated with many steps, it is mainly a simple process of “plan submission => grant application => grant issuance.
- (1) The subject person prepares the “Initiative Business Plan”.
- (2) Consult and submit business plans to the Regional Agricultural Revitalization Council, etc.
- (iii) Consultation and submission of business plans from the council to the prefectures
- (4) Prefectures consult and submit project plans to the national government and fund management organizations
- (5)-(7) National => Prefectural => Council => Target person, and the project plan is approved.
- (viii) The subject person applies to the prefectural government for the grant.
- (ix) Application for grant is made by the prefecture to the national government or the fund management organization.
- (10)-(11) The national government or fund management organization provides grants to eligible recipients through prefectures.
Tent Warehouseへの
Contact us

What you need to know when building a warehouse
We packed it all in.
Clues to solving the 2024 problem
Recommended for
I don't know where to start in building a warehouse.
I want to build a warehouse in an economical way.
Which type of warehouse should we build?
I want to learn the basics of warehouse construction anyway.
I'm concerned about the 2024 problem, but I don't know what to do about it.
Related Articles
- TOP>
- Taiyo Kogyo Column>
- How farmers can improve their earnings by utilizing the MAFF’s “Production Area Production Base Power Up Project”.








