
"Fagot Sheet" for soft ground
Civil engineering sheets with strength and workability used as a bedding material method (fagot method) in reclamation work on soft ground.
Fagot method is a method of surface treatment of soft ground that replaces the sodding and replacement methods, and involves placing sheets to ensure the traveling safety (traficability) of heavy equipment, prevent unequal settlement, and separate soft ground and fill material.
*For sale only in the Japanese market.
Related Achievements
Product & Service
Features
Fagot sheet (PPF)
Lightweight, flexible, resistant to high and low temperatures and silt, and with excellent permeability, this civil engineering sheet can be used for various applications such as soft ground surface treatment and soil layer separation.
| item | Stock number | PP#300 | PP#700 | PP#1212 | Test procedure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Fabric Material | polypropylene | |||||
| Thickness | mm | 0.39 or more | 0.50 | 0.37 | JIS L 1098 | |
| Weight | g/m2 | 120 | 165 | 105 | JIS L 1098 | |
| Tensile strength | N/5cm | vertical | 1180 | 1570 | 1040 | JIS L 1098 |
| … and upwards | horizontal | 1180 | 1472 | 1040 | ||
| elasticity | % | vertical | 17 | 17.5 | 20 | JIS L 1098 |
| … and upwards | horizontal | 13 | 14 | 14 | ||
Note: The above values are measured values, not standard values.
Fagot sheet (PPDX)
Lightweight and portable civil engineering sheet made of polypropylene fiber mesh with a special fiber structure.
| item | Stock number | PP#300 | PP#700 | PP#1212 | Test procedure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Fabric Material | polypropylene | ||||
| Weight | g/m2 | 120 | 135 | 190 | JIS L 1098 |
| Tensile strength | kN/m or more | 32 | 39 | 49 | JIS L 1098 |
| N/5cm or more | 1620 | 1960 | 2450 | JIS L 1098 | |
| Elasticity | % | 17~22 | 17~22 | 18~23 | JIS L 1098 |
Note: The above values are measured values, not standard values.
Main components and installation procedures
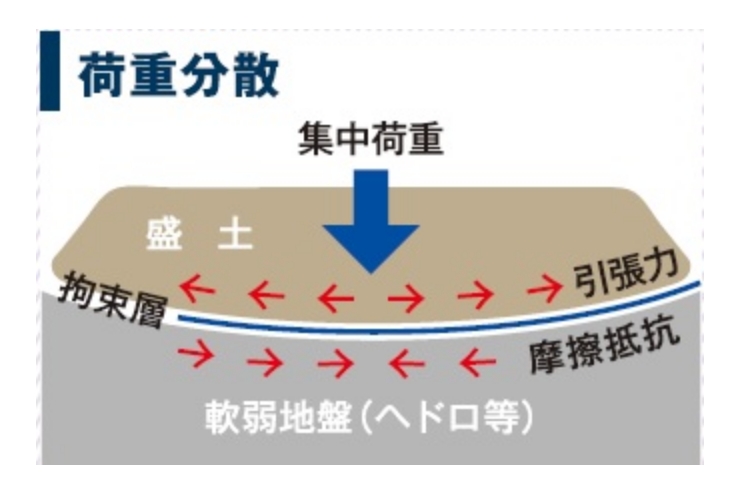
Load distribution
When spreading out high-quality soil and sand by placing civil engineering sheets on the surface of soft ground, the upper load is evenly distributed by the tensile force of the sheets. Ground stability and trafficability can be secured at the same time. (Hammock effect)
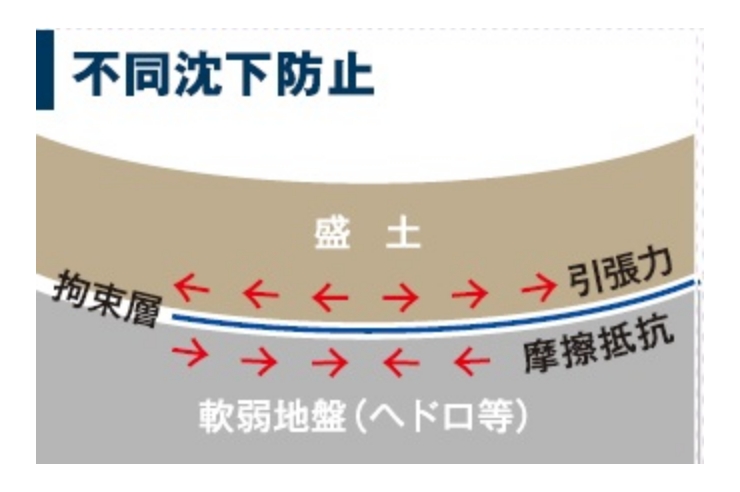
Prevention of unequal settling
The spreading and unequal settlement of overburden loads are constrained by the restraining layer created between the soft ground and the embankment by the placement of civil engineering sheets. Lateral flow of sludge, etc., can also be restrained. (Push-fill effect)
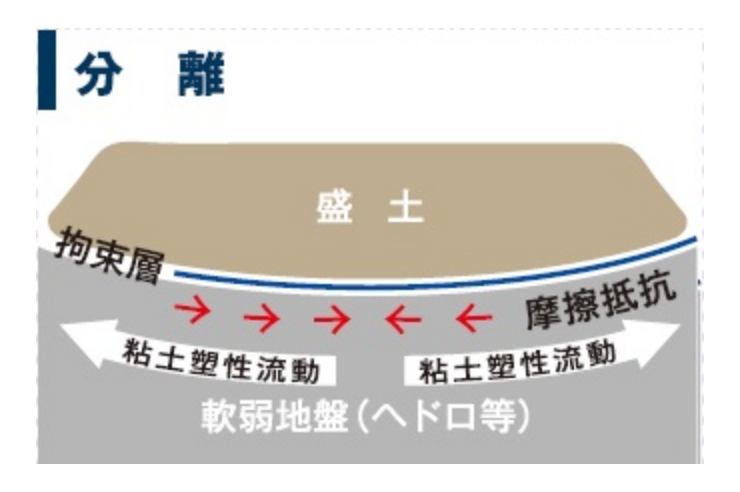
Isolation
After the confining layer is built, it prevents earth and other fill materials from sinking into the soft ground.
Usage
- Soft ground surface treatment (roads, residential land development, reclamation work, temporary roads)
- Soil layer separation (filter material)
- Materials to prevent silt from infiltrating roadbeds
- Filter materials for underground drainage facilities









